 Why, When, and How Ultrasound of the Gallbladder is Performed: A Comprehensive Guide
Why, When, and How Ultrasound of the Gallbladder is Performed: A Comprehensive Guide
The ultrasound of the gallbladder is a medical procedure used to examine the gallbladder and surrounding organs. It is a non-invasive and painless imaging technique that uses sound waves to create detailed images of the internal structures of the body. This procedure is commonly used to diagnose and monitor various conditions related to the gallbladder, such as gallstones, inflammation, and tumors.
There are several reasons why an ultrasound of the gallbladder may be recommended. One of the most common reasons is the presence of symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or jaundice, which may indicate a problem with the gallbladder. Additionally, this procedure may be performed to evaluate the size, shape, and position of the gallbladder, as well as to assess its function.
The ultrasound of the gallbladder is a simple and quick procedure that does not require any special preparation. The patient lies on a table, and a gel is applied to the skin over the abdomen. The ultrasound technician then moves a handheld device called a transducer over the area, which emits sound waves and captures the echoes reflected back from the internal organs. These echoes are then converted into images that can be viewed on a monitor.
The ultrasound of the gallbladder is a valuable diagnostic tool that helps healthcare professionals assess the health and function of this vital organ. By providing detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures, it aids in the diagnosis and management of various gallbladder disorders. If you are experiencing symptoms related to the gallbladder, consult with your healthcare provider to determine if an ultrasound is necessary.
Why Get a Gallbladder Ultrasound
A gallbladder ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder. It is performed to evaluate the structure and function of the gallbladder and to diagnose various conditions affecting this organ.
There are several reasons why a person may need to get a gallbladder ultrasound:
- Suspected Gallbladder Disease: If a person is experiencing symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or jaundice, a gallbladder ultrasound may be recommended to check for gallbladder disease, such as gallstones or inflammation.
- Monitoring Gallbladder Conditions: For individuals who have been diagnosed with gallbladder disease or other conditions affecting the gallbladder, regular ultrasound exams may be performed to monitor the progression of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
- Preoperative Evaluation: Prior to certain surgeries, such as gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy), a gallbladder ultrasound may be done to assess the size, position, and other characteristics of the gallbladder.
- Abnormal Liver Function Tests: If a person’s liver function tests are abnormal, a gallbladder ultrasound may be ordered to investigate possible causes, as the gallbladder is closely related to the liver.
Gallbladder ultrasound is a safe and painless procedure that does not involve exposure to radiation. It provides detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures, helping doctors make accurate diagnoses and treatment plans. If you are experiencing symptoms or have a medical condition that may affect the gallbladder, it is important to discuss with your healthcare provider whether a gallbladder ultrasound is necessary for your case.
Detecting Gallbladder Problems
Ultrasound of the gallbladder is a non-invasive imaging technique that is commonly used to detect and diagnose various gallbladder problems. It is a safe and effective tool that provides detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures.
Some of the common gallbladder problems that can be detected through ultrasound include:
- Gallstones: Ultrasound can detect the presence of gallstones, which are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder. These stones can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- Gallbladder inflammation: Ultrasound can show signs of inflammation in the gallbladder, which can be caused by conditions like cholecystitis or gallbladder infection. Inflammation can cause pain, fever, and tenderness in the upper abdomen.
- Gallbladder polyps: Ultrasound can identify the presence of gallbladder polyps, which are small growths that can develop on the lining of the gallbladder. While most polyps are benign, some may be precancerous or cancerous.
- Gallbladder tumors: Ultrasound can help identify tumors in the gallbladder, including both benign and malignant tumors. Malignant tumors may require further evaluation and treatment.
During an ultrasound of the gallbladder, a transducer is placed on the abdomen. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off the gallbladder and produce images on a computer screen. These images can help detect abnormalities and guide further diagnosis and treatment.
If you experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever, or jaundice, your healthcare provider may recommend an ultrasound of the gallbladder to assess its condition and identify any potential problems. Early detection of gallbladder problems can lead to timely treatment and improved outcomes.
Diagnosing Gallbladder Diseases
Ultrasound of the gallbladder is a common diagnostic procedure used to detect and evaluate various diseases affecting the gallbladder. It is a non-invasive and painless imaging technique that uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures.
Gallbladder diseases can present with a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and changes in bowel habits. In order to accurately diagnose these diseases, imaging tests such as ultrasound are often necessary.
During an ultrasound of the gallbladder, a small handheld device called a transducer is placed on the abdomen. The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves that bounce off the gallbladder and surrounding tissues. These echoes are then converted into images that can be viewed on a monitor.
Ultrasound can help diagnose a range of gallbladder diseases, including:
Gallstones: Ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality for detecting gallstones. These are small, hard deposits that can form in the gallbladder and cause symptoms such as pain and inflammation. Ultrasound can accurately identify the presence of gallstones and their size and location.
Gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis): Ultrasound can help determine if there is inflammation of the gallbladder, which is often caused by gallstones. Inflammation of the gallbladder can lead to severe pain and other complications.
Gallbladder polyps: Ultrasound can detect the presence of polyps, which are abnormal growths that can develop on the lining of the gallbladder. While most gallbladder polyps are benign, some may be precancerous or cancerous.
Gallbladder cancer: Ultrasound can aid in the detection and staging of gallbladder cancer. It can help determine the size and extent of the tumor, as well as whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
In addition to diagnosing gallbladder diseases, ultrasound can also be used to guide certain procedures, such as gallbladder biopsies or the placement of drainage tubes in cases of gallbladder blockage or infection.
Overall, ultrasound of the gallbladder is a valuable tool in diagnosing various diseases affecting the gallbladder. It is a safe and effective imaging technique that provides detailed and accurate information, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions regarding treatment and management of these diseases.
When to Get a Gallbladder Ultrasound
A gallbladder ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging test that uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder. It is typically done to evaluate the structure and function of the gallbladder and to look for any abnormalities or signs of disease.
You may need to get a gallbladder ultrasound if you are experiencing symptoms such as:
- Pain in the upper abdomen: If you have persistent pain in the upper right or middle abdomen, especially after eating fatty or greasy foods, it could be a sign of gallbladder problems.
- Nausea and vomiting: Gallbladder issues can cause nausea and vomiting, especially after eating a meal.
- Jaundice: If your skin or eyes appear yellow, it may indicate a blockage in the bile duct, which could be related to gallbladder disease.
- Unexplained weight loss: If you are losing weight without trying, it could be a symptom of gallbladder problems.
- Fever: A fever may be a sign of inflammation or infection in the gallbladder.
In addition to these symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend a gallbladder ultrasound if you have a history of gallbladder disease, such as gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis). It may also be done as a follow-up test to monitor the progress of a known gallbladder condition.
It is important to discuss your symptoms and medical history with your healthcare provider to determine if a gallbladder ultrasound is necessary for you. The test is safe, noninvasive, and typically does not require any special preparation.
Symptoms Requiring an Ultrasound
An ultrasound of the gallbladder may be recommended if a person is experiencing symptoms that may be related to gallbladder problems. These symptoms can include:
| Abdominal pain | Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) |
| Nausea and vomiting | Fever and chills |
| Changes in bowel movements | Unexplained weight loss |
| Indigestion and bloating | Dark urine |
These symptoms can be indicative of various gallbladder conditions, such as gallstones, inflammation, or infection. An ultrasound can help diagnose the underlying cause of these symptoms and guide further treatment.
Recommended Screening Frequency
The recommended screening frequency for ultrasound of the gallbladder varies depending on the individual’s risk factors and medical history. In general, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound of the gallbladder if you experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, or if you have a history of gallbladder disease.
For individuals with no symptoms or risk factors, routine screening is generally not recommended. However, if you have certain risk factors such as a family history of gallbladder disease, obesity, or age above 40, your healthcare provider may recommend regular screenings every few years.
It is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate screening frequency based on your individual circumstances. They will consider your medical history, risk factors, and symptoms to recommend the most suitable screening schedule for you.
Remember, early detection of gallbladder problems can lead to better outcomes and treatment options, so it is important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for screening.
What to Expect During the Procedure
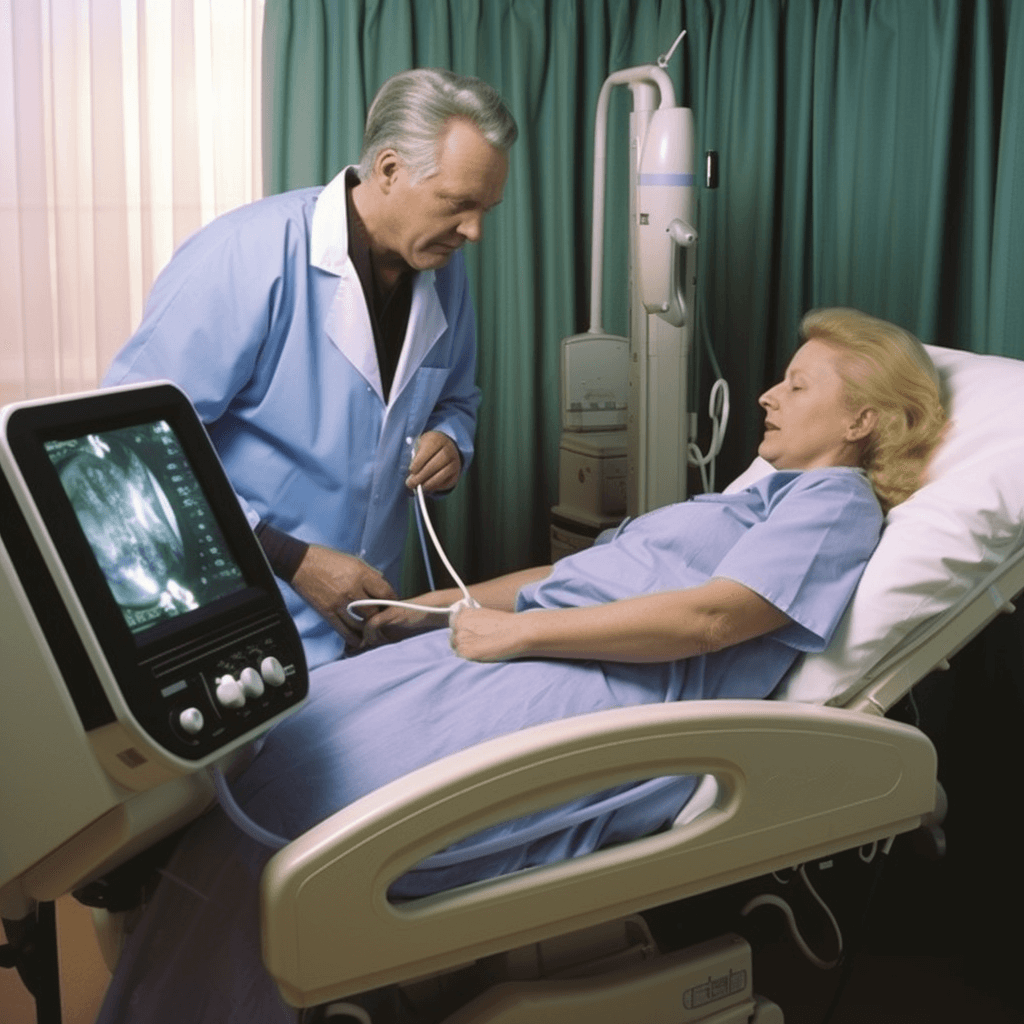
When you arrive for your ultrasound of the gallbladder, you will be asked to change into a hospital gown and lie down on an examination table. The technologist will apply a clear gel to your abdomen to help the transducer make good contact with your skin.
The technologist will then move the transducer over your abdomen, capturing images of your gallbladder from different angles. You may be asked to change positions or hold your breath at times to get better images.
The procedure is painless and usually takes about 15 minutes to complete. You may feel some pressure or discomfort as the technologist presses the transducer against your abdomen, but it should not be painful.
After the procedure, you can resume your normal activities immediately. There are no restrictions or special precautions you need to take.
What to Expect During the Procedure:
| – Change into a hospital gown |
| – Lie down on an examination table |
| – Gel applied to abdomen |
| – Transducer moved over abdomen |
| – Images captured from different angles |
| – Possible position changes or breath holding |
| – Painless procedure |
| – Pressure or discomfort may be felt |
| – Procedure takes about 15 minutes |
| – Normal activities can be resumed immediately |
How the Test is Performed
An ultrasound of the gallbladder is a non-invasive procedure that uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and surrounding organs. The test is typically performed by a trained technician or radiologist in a hospital or imaging center.
During the test, the patient lies on an examination table and the technician applies a gel to the abdomen. The gel helps to transmit the sound waves and improve the quality of the images. The technician then uses a handheld device called a transducer to gently move over the abdomen.
The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off the gallbladder and surrounding structures, creating echoes. These echoes are then converted into images on a computer screen, which can be viewed in real-time. The technician may also take still images or video recordings for further analysis.
Throughout the test, the technician may ask the patient to change positions or hold their breath to obtain better images. The entire procedure usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes to complete.
After the test, the images are reviewed by a radiologist who will interpret the findings and provide a report to the patient’s healthcare provider. The results of the ultrasound can help diagnose conditions such as gallstones, inflammation of the gallbladder, or tumors.
Overall, an ultrasound of the gallbladder is a safe and painless procedure that provides valuable information about the health of the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
Positioning and Duration
During an ultrasound of the gallbladder, the patient is usually positioned lying on their back on an examination table. The technician or radiologist will apply a gel to the abdomen to help with the transmission of sound waves. They will then use a handheld transducer to gently press against the skin and move it over the abdomen to obtain images of the gallbladder.
The duration of the ultrasound examination will vary depending on several factors, including the complexity of the case and the patient’s cooperation. On average, the procedure takes about 15 to 30 minutes to complete. In some cases, additional views or measurements may be necessary, extending the duration of the examination.
It is important for the patient to remain still and breathe normally during the procedure to obtain clear images. The technician or radiologist may also instruct the patient to change positions or hold their breath briefly to capture specific images or assess the gallbladder from different angles.
Overall, proper positioning and cooperation from the patient are essential to ensure a successful ultrasound examination of the gallbladder.
Discomfort and Side Effects
During an ultrasound of the gallbladder, you may experience some discomfort or side effects. However, these are generally minimal and temporary. Some common discomforts or side effects include:
| Discomfort | Side Effects |
| Pressure or mild pain in the abdomen as the ultrasound probe is moved over the gallbladder area. | Allergic reaction to the ultrasound gel or latex if you have an allergy to these substances. |
| Feeling of fullness or bloating due to the need to drink water before the procedure. | Temporary skin irritation or redness at the site where the ultrasound probe is placed. |
| Difficulty lying still for an extended period of time during the procedure. | Discomfort from having a full bladder during the ultrasound. |
If you experience any severe or prolonged discomfort or side effects during or after the ultrasound, it is important to notify the healthcare provider immediately. They can address any concerns and provide appropriate care if necessary.
Q&A:
What is an ultrasound of the gallbladder?
An ultrasound of the gallbladder is a medical imaging test that uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and surrounding organs. It is a non-invasive procedure that can provide detailed information about the structure and function of the gallbladder.
Why is an ultrasound of the gallbladder done?
An ultrasound of the gallbladder is done to evaluate the gallbladder for any abnormalities such as gallstones, inflammation, or tumors. It can also help diagnose conditions like gallbladder disease or cholecystitis and guide further treatment.
How is an ultrasound of the gallbladder performed?
An ultrasound of the gallbladder is typically performed by a trained technician or radiologist. The patient lies on a table, and a gel is applied to the abdomen to help transmit the sound waves. A transducer is then moved over the abdomen, emitting sound waves that bounce off the gallbladder and create images on a monitor.
When is an ultrasound of the gallbladder recommended?
An ultrasound of the gallbladder may be recommended if a patient is experiencing symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or jaundice. It is also commonly performed as part of a routine check-up for individuals at risk of gallbladder disease, such as those with a family history or a history of gallstones.
Is an ultrasound of the gallbladder a painful procedure?
No, an ultrasound of the gallbladder is a painless procedure. The gel applied to the abdomen may feel slightly cold, but the actual ultrasound itself is not painful. It is a safe and non-invasive test that does not involve any radiation.
What is an ultrasound of the gallbladder?
An ultrasound of the gallbladder is a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the gallbladder and surrounding organs.
Why is an ultrasound of the gallbladder done?
An ultrasound of the gallbladder is done to evaluate the gallbladder for conditions such as gallstones, inflammation, infection, tumors, and other abnormalities.
How is an ultrasound of the gallbladder performed?
An ultrasound of the gallbladder is performed by applying a gel to the abdomen and then using a device called a transducer to send sound waves through the body. The sound waves bounce off the gallbladder and other organs, and the echoes are converted into images that can be seen on a computer screen.
When should I have an ultrasound of the gallbladder?
You may need an ultrasound of the gallbladder if you are experiencing symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or if your doctor suspects you may have a gallbladder problem based on your medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will be able to determine if an ultrasound is necessary based on your specific symptoms and situation.